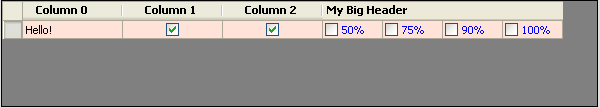
Rectangle hcRct = grid1.GetCellDisplayRectangle(hc.ColumnIndex, -1, true); The first line of code should be self-explanatory. In the second line, we're getting a Rectangle object based on the cell in question. Passing the column index and the row index ("-1" means the row header) to the DataGridView's GetCellDisplayRectangle() method gets us there. Next, we'll use that Rectangle object to get another Rectangle that represents the entire area to be covered by our new Multi-Column-Header. We can do that like so: int multiHeaderWidth = grid1.Columns[hc.ColumnIndex].Width + grid1.Columns[hc.ColumnIndex + 1].Width + grid1.Columns[hc.ColumnIndex + 2].Width + grid1.Columns[hc.ColumnIndex + 3].Width; Rectangle headRct = new Rectangle(hcRct.Left, hc.ContentBounds.Y + 2, multiHeaderWidth, grid1.ColumnHeadersHeight);
headRct.Height -= 3; As you can see, the first line above simply gets the total width of all four columns to be spanned. We then pass that variable along with the other three coordinates (left, top, and height) required to instantiate a Rectangle object. (We add 2 to the Y coordinate and subtract 3 from the Rectangle's height in the next line to create a margin, so that our header cell's top and bottom borders are still visible.)
Next we need to find the size our string will be based on its length and the font we'll be using: SizeF sz = e.Graphics.MeasureString("My Big Header", grid1.Font); Then we figure out where the top will need to be in order to make it vertically centered: int headerTop = Convert.ToInt32((headRct.Height / 2) - (sz.Height / 2)) + 2; Then we set the background color to match the grid's header color: e.Graphics.FillRectangle(new SolidBrush(SystemColors.Control), headRct); And finally, we draw the text, starting 2 pixels to the right of the left-most point of our rectangle so it looks nice: e.Graphics.DrawString("My Big Header", grid1.ColumnHeadersDefaultCellStyle.Font, Brushes.Black, hcRct.Left + 2, headerTop); Read more: C# Corner



0 comments:
Post a Comment